Java 1.8 Priority Queue 代码分析
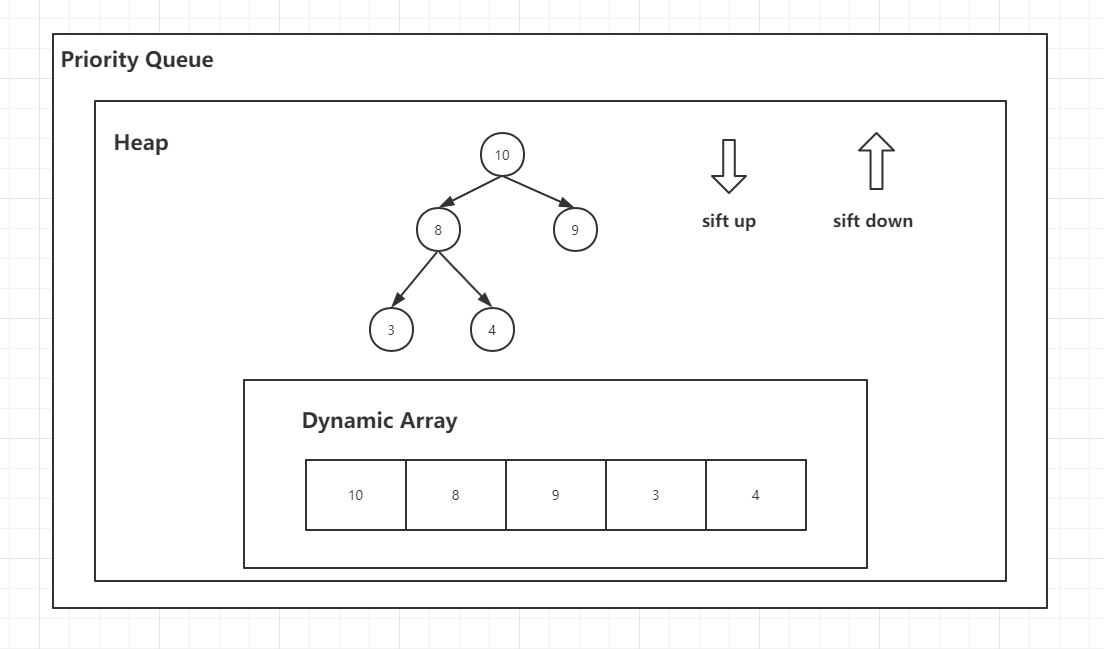

在实际生活中,队列都是有优先级的,在某些条件下不一定按照先到先得,而是按照元素的某些特性进行出队的。
- 比如游戏中 小兵的攻击并不固定,而是攻击离它最近的单位,或者是攻击血量最小的单位。
- 在医院排序看病,医生也会根据患者的患病程度进行就诊,先救治特别紧急的患者。
# 为什么需要优先队列?
按照优先队列的性质,每次出队取最符合“条件”的元素。
那其实也不一定需要优先队列,我用数组,或者链条其实也能实现,只不过我在添加元素的时候对元素进行排序就可以了。这样不是也能解决问题吗?
时间复杂度对比:
普通线性结构:入队 O(1) 出队 O(n)
顺序线性结构:入队 O(n) 出队 O(1)
堆:入队O(logn) 出队 O(logn)
优先队列可以解决什么问题?
- 在 M 个元素中,找出前 K 个元素
# Java 1.8 的底层采用最小[堆](./数据结构 - 二叉堆.md)进行实现。
比较器
PriorityQueue 构造函数中允许传入比较器用于组装堆。在初始化时便可以传入比较器。
PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1); q.add(1); q.add(2); q.add(3); Integer result = q.peek(); System.out.println(result); // 3添加元素
优先队列中添加元素实际上是在堆中添加元素时间复杂度为 (logn).
// 添加指定的元素到优先队里中 public boolean add(E e) { return offer(e); } public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); modCount++; int i = size; if (i >= queue.length) grow(i + 1); size = i + 1; if (i == 0) queue[0] = e; else siftUp(i, e); return true; }添加元素时,首先判断当前容器是否还能承载新元素,如果不能则进行扩容操作
grow如果当前堆中不还没有元素则直接添加即可,否则进行 Sift Up (上浮) 操作。
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x; while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = queue[parent]; if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = key; }实际就是进行上浮,与父节点进行对比,迭代交换
取出 “最符合条件”的元素
添加元素的时候,其实就是已经形成了最符合条件的堆(最大堆|最小堆),根节点其实就是将要取出的节点,后续我们只需要进行 堆的下浮(Sift Down)即可。
public E poll() { if (size == 0) return null; int s = --size; modCount++; E result = (E) queue[0]; E x = (E) queue[s]; queue[s] = null; if (s != 0) siftDown(0, x); return result; }private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) c = queue[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) break; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = key; }
← 数据结构 - 二叉树 数据结构 - 堆 →